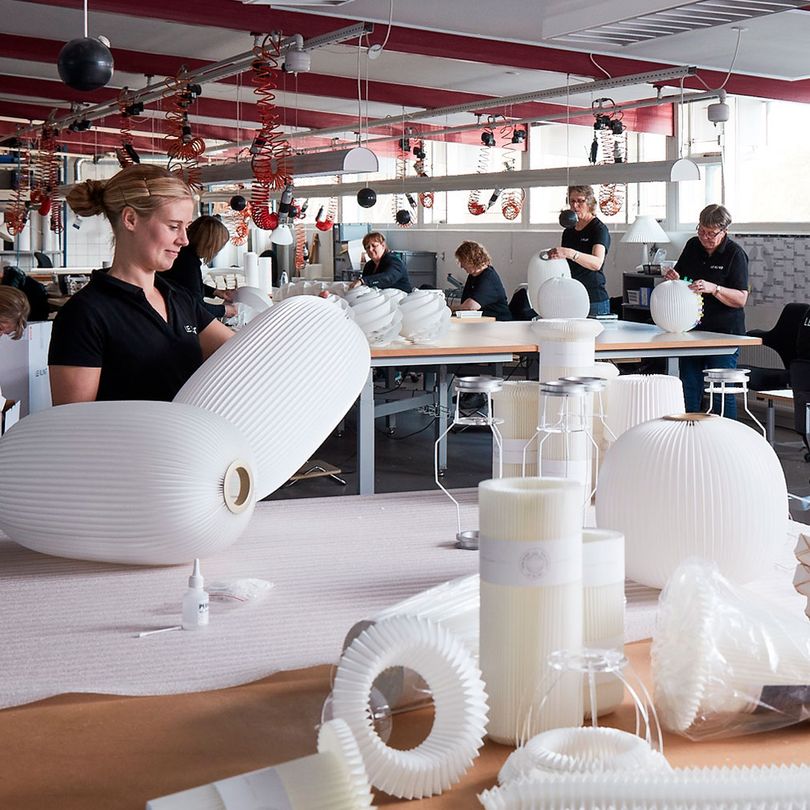
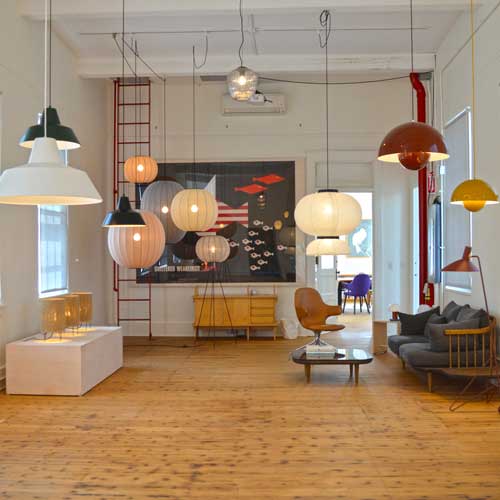
Midgard - Curt Fischer & the First Articulating Lamp
The early 20th century inventor and designer Curt Fischer spent time researching ways in which he might be able to improve the light quality in his town's factories during the 19-teens. Upon visiting and speaking with the workers, it was discovered that the downward-casting overhead lighting created shadows on their work surfaces. And so the first articulating lamp was designed and patented. Used on the wall or desktop, this adjustable lamp even allows for an optional asymmetrical rotatable shade to block direct light from the user's eye.

The man whose lamps lit both the metal workshop and the artists’ studios at the Bauhaus started his career as the owner of an engine works: Curt Fischer, today regarded as one of the greatest 20th-century inventors. In 1919, he took over the Industriewerk Auma based in Thuringia. He added “Ronneberger und Fischer” to the company’s name in commemoration of Konrad Ronneberger who had established the factory in 1912 and had been killed three years later in the war.
With the end of WWI, industrialisation picked up pace again. People worked long hours until late in the evening. The then-typical lamps cast light from above only, with the effect that the shadow of the worker’s body and head would obscure the piece he was working on. For an inventor like Curt Fischer, who had transformed horse-drawn coaches into mobile radio stations during the war and who had participated in the development of the communication devices for the Zeppelin, this situation posed an intriguing challenge. It wouldn’t take him long to come up with a solution: in November 1919, his famous Scherenleuchte (Scissor-arm Lamp) was born, soon to be followed by other new types of lamps: the Lenklampen (Adjustable Lamps) with the model numbers 113 and 114, both of which would soon be found in the metal workshop of the Dessau Bauhaus, and the Maschinenleuchte (Machine Lamp).

With the development of these adjustable lamps, Curt Fischer became the inventor of directional light. But that wasn’t all: in 1922, he created the first glare-free reflector (rotatable and asymmetrical) for perfectly directed light. Walter Gropius was a big fan of the Midgard lamps. He and Fischer exchanged letters between 1927 and 1931. Gropius’ successor at the Bauhaus in Dessau, Hannes Meyer, was just as thrilled and had the reading rooms of the General German Trade Union Confederation in Bernau near Berlin fitted with Midgard lamps